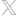Demand for H-1B Visas in New England: An Analysis of Employer Requests for Highly-Skilled Guest Workers 
The H-1B visa program allows employers to hire guest workers in "specialty occupations" and allows these workers to apply for permanent residency while working on the temporary visa. Some immigration reform advocates argue for an increase in the number of H-1B visas to address a shortage of STEM labor and to allow businesses to compete globally for the "best and brightest" talent. Others argue against increasing the availability of such visas for fear the program allows firms to employ guest workers at lower wages than domestic peers and is heavily used by outsourcing firms to transfer jobs to less costly destinations.
This debate about the role of H-1B visas is based almost entirely on analysis at the national level. To better inform policy discussions in New England this report provides new insights into the geographic variation of demand for H-1B visas, the types of workers requested and their regional concentrations, and the types of employers that demand H-1B visas in the region.
This report finds that New England has some of the highest levels of demand for H-1B workers nationwide, relative to employment, due to significant demand from a few metropolitan labor markets in Connecticut and Massachusetts. This analysis also shows that there are various intended uses of the H-1B visa: it is not solely used to address a STEM-skills shortage nor is it used principally to outsource work to less costly locations. Finally, the report recommends developing a clearer policy goal for the H-1B visa program, which would support more coherent criterion for admitting highly skilled guest workers and provide a context within which to determine the desired admission levels of the program.

 Resources
Resources
Appendices
Data By Metro Area
Select a Metro Area:
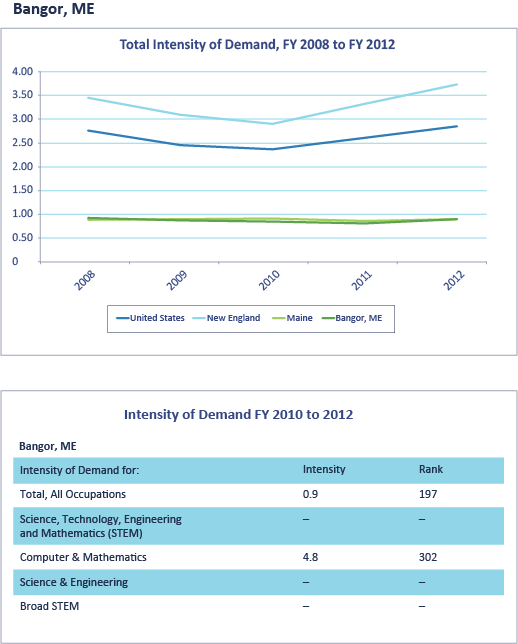
Source: Office of Foreign Labor Certification LCA database, and CareerOneStop Employer Locater available through the U.S. Department of Labor, Employment and Training Administration based on proprietary data purchased from Inforgroup.
Notes: Intensity of demand represents Labor Condition Application requests per 1,000 payroll employees. Requests are average annual requests for FY 2010–2012. The primary location of requests is based on the most common location from which the firm was listed as requesting visas in the LCA. This does not necessarily indicate that the firm is headquartered there. All requests listed in this table are for H-1B workers in New England. Industry titles are based on four-digit NAICS codes. Employment by location for employers is provided with a range. The values here are the sum of employment ranges for each firm in the six New England states, standardized to the employment ranges provided by the U.S. Department of Labor. See the on-line data appendix available the report’s index page for additional information about requests of the top employers regionally and nationally.”
Forum
Improving High-Skill Immigration Policy for New England: A regional perspective on demand for H-1Bs visas and an exploration of potential policy improvements
This October 2014 forum featured the policy report profiled above. Author and keynote speaker, Robert Clifford, presented new research profiling the demand for H-1B visas in New England and its major metropolitan areas. Panelists discussed the extent to which the program is accomplishing its intended goals and explore policy reforms that could promote better policy outcomes.
Related Research
Foreign Nurse Importation to the United States and the Supply of Native Registered Nurses
by Patricia Cortés and Jessica Pan
Working Paper No. 14-7
Immigrants as a Potential Source of Growth for New England’s Highly Skilled Workforce
by Tara Watson, Visiting Scholar
NEPPC Policy Brief 13-4
Enforcement and Immigrant Location Choice
by Tara Watson
Working Paper No. 13-10
A Portrait of New England's Immigrants
by Antoniya Owens
NEPPC Research Report 08-2